
collections.Counter()
파이썬 collections 모듈의 Counter클래스를 사용하면
동일한 값의 데이터가 몇 개 들어갔는지 딕셔너리 형태로 출력한다.
예 )
collections.Counter(['java','파이썬','python','자바','C','파이썬','자바'])

collections.Counter({'pyton':5, 'C':6})

변수에 넣어서 사용하기
collections.Counter()를 변수에 선언하고 값을 넣으려면 update()를 사용해야한다. :
cnt = collections.Counter()
cnt.update('간장공장공장장')
cnt
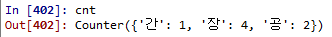
위와 같은 상태로 update를하면 value값이 더해진다. :
cnt.update({'간':10,'장':20})
cnt

딕셔너리 형태이므로 key와 value를 따로 뽑아낼 수 있다. :
for k,v in cnt.items() :
print(k,v)
cnt.keys()
cnt.values()

elements()를 사용하면 value값 만큼 key를 뽑아낸다. :
cnt.update({'간':-10,'장':-20})
list(cnt.elements())

collections.Counter().most_common()
빈도수가 가장 많은것 순으로 뽑아낸다. 괄호안에는 몇개를 뽑을지 입력한다.
cnt.most_common(1)
cnt.most_common(2)

collections.Counter() 연산
cnt1 = collections.Counter(['p','y','t','h','o','n'])
cnt2 = collections.Counter('pythonpytorch')
cnt1
cnt2

1) 덧셈(+)
cnt1 + cnt2

2) 합집합( | )
cnt1 | cnt2

3) 뺄셈 (-)
cnt1 - cnt2
cnt2 - cnt1

4) 차집합 (&)
cnt1 & cnt2

map
for문을 사용하지 않고 리스트의 요소를 지정된 함수로 처리해주는 함수이다.
def f1(arg):
return arg * 3
f1([100,200,300])

[f1(i) for i in [100,200,300]]

list(map(f1,[100,200,300])) #위의 for문의 기능을 대신해줌

'컴퓨터 > 파이썬' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 파이썬(Python) - Pandas와 DataFrame (0) | 2020.03.10 |
|---|---|
| 파이썬(Python) - Pandas와 Series (0) | 2020.03.09 |
| 파이썬(Python) - 파일 열기 모드 / with문 (0) | 2020.02.26 |
| 파이썬(Python) - 날짜 / 달력 관련 라이브러리 (0) | 2020.02.25 |
| 파이썬(Python) - 파이썬 파일(.py) 저장 및 불러오기 (0) | 2020.02.25 |